Fish Monitoring
Fish monitoring will help our environmental unit to understand fish abundance, fish movement and fish health above and below the slide site. Fish monitoring will allow for the quantification of the migration time for individual fish of select species, size and sex. The First Nations Leadership Panel has supported fish monitoring and capture techniques via consensus amongst leaders.
What fish monitoring methods are being used for?
- Hydroacoustic monitoring
- Radio tag monitoring
- Blood sampling
How does hydroacoustic monitoring work?
Hydroacoustic monitoring uses sonar technology to monitor fish underwater. Experts can continually track and monitor fish’s location through acoustic sound vibrations as they reach a specified target. This method of monitoring helps track and monitor fish positions around the slide site. Hydroacoustic monitoring stations are set up below and above the slide site for data collection. This can provide insight into the number of fish attempting to pass through the site.
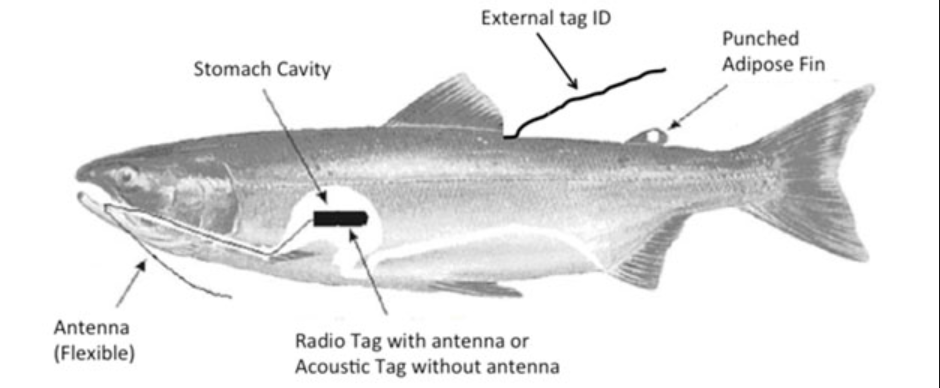
How do radio tags work?
Radio tags are inserted into a fish’s stomach. The tag is harmless to migrating fish because as they move upstream, they do not eat. The radio tag emits a signal that is then received by a shore-based receiver. Resulting data, collected by the shore-based receiver, will inform the environmental unit on the survival success rate of the fish, once they reach their terminal spawning grounds.
What is the purpose of blood sampling?
A small sample of blood above and below the slide will be collected to help the environmental unit assess the energy reserves of the fish once they have passed the obstruction. Blood samples will measure the bioenergetic markers of the fish. This will help to determine their bioenergetic condition once they arrive at their migration spawning grounds.
What fish capture techniques are being used to support monitoring efforts?
The most frequently used method for capturing fish for monitoring purposes in the area is beach seining. Extreme flood conditions upstream the slide site are depositing significant amounts of debris into the water. This is making beach seining capture difficult and dangerous for personnel. Contingency capture techniques are being considered, including dip netting, fish wheels, and diversion weirs.
