Data methods for the Community Energy and Emissions Inventory
The methods used to establish Community Energy and Emissions Inventory (CEEI) reports are based on community-level needs and available data. The methods are continually improving with the intent to increase alignment with provincial and national energy and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions data sets.
Since CEEI reports use different methods from other provincial-level GHG emissions reporting, it's not appropriate to make direct comparisons or share data between these data sets.
Read more:
- B.C. Best Practices Methodology for Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions (PDF, 1.1MB)
- Emission Factors Catalogue (XLSX, 392KB)
- Technical Methods and Guidance Document for CEEI, 2017 (PDF, 1.7MB)
- Global Protocol for Community-Scale Greenhouse Gas Inventories (PDF, 24.7MB)
Data included in the inventory
Data by sector
Data is provided for GHG emissions and energy use that are:
- Created within a jurisdiction (Scope 1)
- Caused by grid-supplied electricity, heat, steam and/or cooling within a city (Scope 2)
Data inputs
- GHG emissions are calculated based on energy consumption in buildings and indirect GHG emissions from purchased electricity and stationary fuel combustion. Community-level consumption and GHG emissions for heating oil, propane and wood is derived by:
- Estimating the total energy required for heating and other uses
- Subtracting the electricity and gas consumption from this total
- Assigning the remainder as heating oil, propane or wood, using other available data to estimate how much for each
- Electricity, natural gas and piped propane use are based on consumption data provided by utility companies
- Consumption data uses the following units of measure:
- Kilowatt hours (kWh) for electricity
- Gigajoules (GJ) for all other fuel types
Note: You can find a full list of data inputs in the Read me section of the buildings data sets.
Data partners
- BC Hydro
- Big White Gas
- Cal-gas
- City of Grand Forks
- City of Kelowna
- City of New Westminster
- City of Penticton
- City of Summerland
- FortisBC
- Nelson Hydro
- Pacific Northern Gas
- Port Alice Gas
- Silversmith Power and Light
- Star Gas
- Sun Peaks Utilities
- Yukon Electric
Data inputs
- GHG emissions from on-road transportation for a local government are given by:
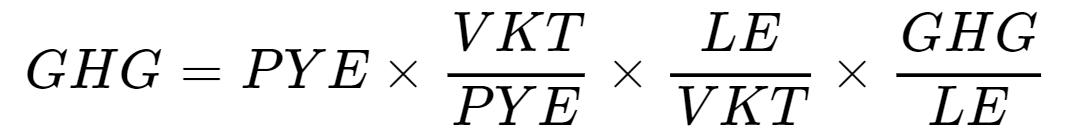
- Vehicle populations (PYE) are estimated using vehicle registration data from the Insurance Corporation of British Columbia
- Vehicle Information Numbers are used to categorize vehicles by type
- Estimates of vehicle kilometres travelled (VKT) per vehicle (VKT/PYE) are based on vehicle registration, population, AirCare and trip diary data
- Fuel usage, measured as litres equivalent (LE) is converted to fuel economy (LE/VKT) using fuel economy data taken from Natural Resources Canada
- Emissions factors from the National Inventory Report are used to convert litre equivalents of fuel into GHG emissions
- Read more: New Provincial On-Road Transportation Methodology (PDF, 157KB)
Note: You can find a full list of data ranges and providers in the Read me section of the transportation data sets.
Data partners
- Insurance Corporation of British Columbia
- Natural Resources Canada
- Environment and Climate Change Canada
Data inputs
- Municipal solid waste (landfills) GHG emissions are based on estimates of landfill gas production calculated from the mass of solid waste tipped at landfills
- Two different methodologies have been used:
- Waste-in-place (WIP) estimates the actual annual GHG emissions from a landfill based on the decomposition of all municipal solid waste previously disposed at the landfill
- Waste commitment estimates the GHG emissions from solid waste deposited in a landfill for a specific year. It does not include solid waste data from previous years. This data point is useful when comparing data between jurisdictions
-
Read more: CEEI Technical Methods and Guidance Document for CEEI Reports (PDF, 1.7MB) > Section 7 Municipal Solid Waste Sector
Note: You can find a full list of data ranges and providers in the Read me section of the solid waste data sets.
Data partners
Internal consumption data is provided by:
- B.C. Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy
- Regional district staff
- Other resource materials
Data available by year
|
Year |
Buildings |
Transportation |
Waste |
|
2007 |
|
||
|
2008 |
|||
|
2009 |
|||
|
2010 |
|||
|
2011 |
|||
|
2012 |
|||
|
2013 |
|||
|
2014 |
|||
|
2015 |
|||
|
2016 |
|||
|
2017 |
|||
|
2018 |
|||
|
2019 |
|||
|
2020 |
|||
|
2021 |
Units of measure
Standard unit
The unit used to report GHG emissions is “equivalent CO2” (CO2e) in units of mass. The unit of mass depends upon the scale of the emissions. CEEI reports GHG emissions in tonnes CO2e.
Emission factors
Emission factors are expressed in kilograms (kg) or metric tonnes (t) of GHG emissions per unit of consumption activity.
Using common units across activity categories makes it easier to compare data. For example, if building energy or fleet fuel consumption are expressed in common units, you can compare data across different fuel types, travel modes, etc.
Read more about emission factors:
Global warming potential (GWP)
Used to compare the ability of different GHGs to trap heat in the atmosphere (radiative forcing).
- The GWP from the release of 1 kg of CO2 equals 1
- The GWP of other GHGs is stated relative to CO2
CEEI reporting uses the Fifth Assessment Report GWPs as recommended by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change for the major gases and groups of gases.
Contact information
Our team of experts can answer questions or provide info about how to use the data. You can also let us know if you have data or methods you'd like to share.
