Road Weather Information System - Data Definitions
Find data definitions for the Road Weather Information System (RWIS).
Note: Not all sensors are installed at every station. A data value of -99 indicates that the sensor is either not present or that it is reporting invalid data.
Viewing the Data
There are now 2 separate web sites for accessing the data from the Ministry’s Weather Network. The original site at https://prdoas5.apps.th.gov.bc.ca/saw-rwis is still active, and still includes all stations in the network. The newer “RWIS Optical” site at https://rwis-optical.th.gov.bc.ca now has the data from all stations in the Ministry’s Weather Network (Road Weather Stations and Avalanche Weather Stations).
There are now 25 “Next Generation” Road Weather Stations, making up one quarter of the Road Weather Network. For more information see Next Generation Weather Stations.
Road Surface Data
Road Temperature and Condition Data can come from either of 2 types of Pavement Sensor: the older style embedded sensor (“’pavement puck”), or the newer Optical Pavement Sensors (now installed at 72 Road Weather Stations).
Embedded pavement sensors provide the following data as presented on the original RWIS web site:
Freezing Point
An estimate of the temperature at which moisture on the road surface would freeze. It is based on measurements of conductivity across the surface of the sensor. Freezing point is difficult to measure accurately, and there must be some moisture present for a reading to be obtained. Data is displayed to the nearest whole degree. The sensor’s calibration is based on a solution of Sodium Chloride. If different salts are applied, the estimates of Freezing Point will be less reliable.
Surface Temperature
Temperature of the asphalt surface, as measured at the top of the hour. Data is displayed to +/- 0.1°C precision and is considered accurate to within 0.2°C. There are 2 sources of surface temperature data. The Primary sensor is the most accurate. The Alternate sensor is intended as a backup in case of failure of the Primary sensor.
Dew Point
The temperature to which the air would have to be cooled to reach saturation (100% relative humidity). Dew point is calculated based on the relative humidity (RH). RH is difficult to measure accurately, especially for temperatures near or below freezing, so dew point is only displayed to the nearest whole degree.
If the Surface Temperature is lower than the Dew Point then moisture from the air can condense onto the pavement surface (liquid dew if temperature is above freezing, or frost or black ice if temperature is below freezing).
Sub Temperature (only available in ‘Data Table’ or ‘Download’)
The temperature within the road bed as measure by a thermistor at a depth of approximately 25 cm below the pavement surface at the top of the hour. Data is displayed to +/- 0.1°C precision and is considered accurate to within 0.2°C.
Road Status (only available in ‘Data Table’ or ‘Download’)
The pavement sensor expresses whether the sky is clear or cloudy (using a fibre optic ‘eye’), and whether the pavement is dry, moist, wet, slushy, snowy, or icy. A ‘wet and chemical’ condition indicates that a salt solution is present on the road surface. A ‘warning’ condition indicates that potentially slippery road conditions are possible. An ‘alarm’ condition indicates that slippery conditions exist.
Data from Optical Pavement Sensors is described below:
Optical Pavement sensing will eventually replace the traditional embedded pavement sensors, or ‘pucks’. The system consists of a pair of sensors; one is a highly accurate infrared temperature sensor for measuring pavement surface temperature, and the other is a multi-channel spectral instrument that senses the surface condition of the pavement, the thicknesses of water, snow, or ice that may be present, and then uses these to estimate a pseudo co-efficient of friction (‘Level of Grip’). Finally, a ‘Road Status’ is output that describes the surface condition, and may include Warnings or Alarm conditions depending on how slippery the surface is.
The data from optical pavement sensors is presented on a separate web site dedicated to these sensors.
The URL is: https://rwis-optical.th.gov.bc.ca
To gain access to this site, simply visit the URL above, click on the link to “Create Account” and submit the form that pops up.
The data consists of the following categories:
- Air Temperature and Dew Point Temperature
- Pavement Surface Temperature
- Surface Coverage Thickness values of water, snow, and ice if present (in mm of thickness). For snow, the value is the water equivalent of that layer of snow.
- Level of Grip (Dry pavement generally 0.82, Icy Surface as low as 0.09, other surface conditions fall in the range between those extremes). This is determined from the Surface Coverage Thickness values.
- Surface Condition (Dry, Moist, Wet, Frosty, Snowy, Slushy, Icy)
- Warning or Alarm conditions are associated with the Surface Condition depending on the range of Level of Grip. If the Level of Grip falls below 0.6, then a Warning is associated with the Surface Condition, and if the Level of Grip falls below 0.4 then an Alarm is associated with the Surface Condition.
Air Data
Air Temperature
The air temperature as measured by a thermistor mounted in a shield on the station tower at the top of the hour. Data is displayed to +/- 0.1°C precision and is considered accurate to within 0.2°C.
Maximum and minimum temperatures are recorded over 12 hour periods beginning at 0600 hrs and 1800 hrs (only available in ‘Download’).
Relative Humidity (RH)
RH compares the amount of water vapour in the ambient air to the amount of vapour that air at that temperature could hold if it were saturated, expressed as a percentage. If air with 100% RH is cooled then the moisture will condense out as liquid (above freezing) or sublimate out as ice crystals or black ice (below freezing).
Snow and Precipitation Data
Snow and Precipitation data can come from either of 2 classes of instrumentation. Stations installed before 2017 have Precipitation Gauges, Snow Depth Sensors, and Precipitation Detectors. Stations installed since 2017 use a Present Weather Sensor, and the data from these sensors is described in the section on Next Generation Weather Stations.
The following section describes the data from the sensors at stations installed prior to 2017, and their presentation on the original RWIS web site:
The Precipitation Graph can be toggled to show Snow Data, Precipitation Gauge Data, or both.
Snowpack
The depth of snow on the ground in centimetres as measured by an ultrasonic sensor mounted on an arm from the tower. A series of measurements are taken near the top of the hour, and an average of those is presented after some statistical manipulation.
New Snow
An estimate of the amount of new fallen snow in centimetres in the period since 0600 or 1800 hours. It is based on the change in the depth of the snowpack, and adjustments are taken into account for settling of the snow based on temperatures.
Hourly Precipitation
The change over the past hour in the depth of liquid in a precipitation gauge (in mm), measured once every hour by a pressure transducer. Temperature change and other factors (including evaporation from the gauge) can affect the transducer, so fluctuations up and down can be seen during dry weather at some sites. In the case of snowfall, precipitation is the water equivalent of the snow that accumulated in the gauge during the hour.
New Precipitation
The accumulation of hourly precipitation (measured in mm) in the period since 0600 or 1800 hours.
Precip Detector Ratio
The Precipitation Detector is an optical instrument that gives a “yes / no” data point at the end of every 95 second time interval depending on whether precipitation was detected or not. Each hour, this data is summarized to express the portion of the past hour in which precipitation was detected (ratio is on a scale from 0.00 to 1.00).
Wind and Pressure Data
Wind Speed
The wind speed is measured every 5 seconds over the full hour, then averaged. Displayed in kilometres per hour.
Wind Direction
The wind direction is measured every 5 seconds over the full hour, then averaged, in degrees relative to True North. On the Wind / Pressure graph, direction is displayed as arrows aligned with the direction that the wind is blowing.
Atmospheric Pressure
The atmospheric pressure at the station measured at the top of the hour in millibars (mb). One millibar is equivalent to one hectopascal (hPa). The pressure tendency (trend over the last 3 hours) is a valuable indicator of imminent changes in weather.
Forecast
The Pavement Forecast graph displays the forecast pavement surface temperatures (blue line) for a 24-hour period from the time of issue (either 0500 hrs for the morning issue, or 1500 hrs for the afternoon issue). Each hour, the actual measured pavement surface temperature (red symbols) is added to the graph. New forecasts are generally loaded between 0200 and 0500 hours for the morning issue, and between 1300 and 1500 hours for the afternoon issue.
Across the top of the graph, a series of codes give the forecast pavement condition for each hour of the forecast period (conditions that are forecast to exist in the absence of any road maintenance activities):
DR - dry
LD - light dew
HD - heavy dew
WE - wet
WP - wet and precipitating
LF - light frost
HF - heavy frost
IC - ice
SN - snow
The text forecast below the forecast graph describes the expected weather at the station for the next 3 days.
Instrumentation at Next Generation Road Weather Stations
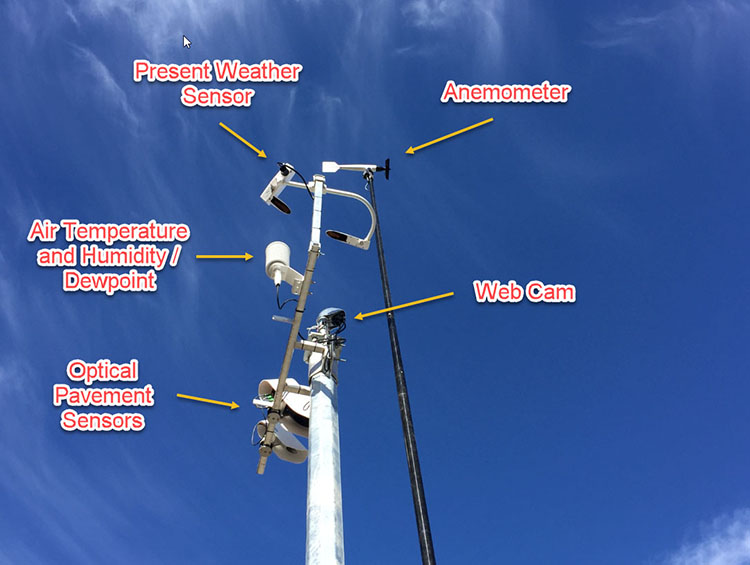
New stations in the network have different instrument arrays than the traditional RWIS stations. The sensors are:
- Optical pavement sensors
- Air temperature and humidity sensors
- Present Weather Detectors
- Some but not all stations have anemometers (wind speed and direction)
- Some but not all stations have barometric pressure sensors
Most of the data is presented on the regular RWIS web site https://prdoas5.th.gov.bc.ca/saw-rwis. However some of the data cannot be displayed on that site, and we recommend using the Optical Sensors’ web site https://rwis-optical.th.gov.bc.ca. A fourth graph has been added to the interface on this site specifically to display the data from the the Present Weather Sensors.
The Present Weather Sensor is a modern instrument that reports a Present Weather Code, precipitation type, precipitation intensity and accumulations, and an accurate visibility measurement.
Present Weather Code: a description of the average weather conditions at the site during the last 15 minutes. If precipitation is occurring, the description includes the precipitation type (eg. drizzle, rain or rain showers, snow or snow showers, or mixed rain and snow), and an intensity category (light, moderate, or heavy). See full listing of the Present Weather Codes below.
Precipitation: Hourly and New precipitation amounts are reported, similar to a precipitation gauge at any of the original RWIS stations (water equivalent in mm).
Snow: Hourly and New snow amounts are reported, similar to a snow depth sensor at any of the original RWIS stations. Depth of snow on the ground (“Snowpack”) is not measured however.
Visibility: The Present Weather Detector uses a forward scatter sensor to measure visibility (m) with a maximum range of 2,000 m.
1 Next generation station at
Pothole Lake on Hwy 97C

2 Instrumentation at
Next Generation Weather Stations

|
No significant weather observed Haze or smoke or dust in suspension, visibility >= 1km Haze or smoke or dust in suspension, visibility <= 1km Mist Fog PRECIPITATION Drizzle (not freezing) or snow grains Rain (not freezing) Snow FOG, visibility <= 1km Fog or ice fog, in patches Fog or ice fog, decreasing last hour Fog or ice fog, no change last hour Fog or ice fog, increasing last hour PRECIPITATION Precipitation, slight or moderate Precipitation, heavy DRIZZLE Drizzle, not freezing, slight Drizzle, not freezing, moderate Drizzle, not freezing, heavy RAIN Rain, light Rain, moderate Rain, heavy Mixed rain and snow, light Mixed rain and snow, moderate or heavy SNOW Snow, light Snow, moderate Snow, heavy Showers or Intermittent Precipitation Rain Showers, Light Rain Showers, Moderate Rain Showers, Heavy Rain Showers, Violent Snow Showers, Light Snow Showers, Moderate Snow Showers, Heavy |
|---|
4 Sample screenshot from
https://rwis-optical.th.gov.bc.ca web site
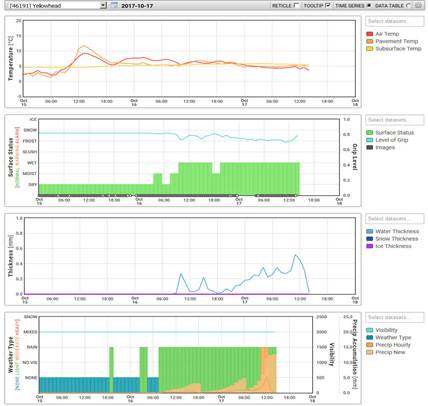
Graph 1: Air and Pavement Temperatures
Graph 2: Pavement Surface Status and Level of Grip with embedded web cam images
Graph 3: Pavement Surface Coverage Thicknesses (water, snow, and ice)
Graph 4: Present Weather Detector data. Visibility, Weather Type, Hourly Precipitation and New Precipitation
Locations of the Next Generation Road Weather Stations (October 2020)
- 22095 Annis Pit: Hwy 1, 8 km southeast of Sicamous
- 24093 Bromley Rock: Hwy 3, 1 km south of Bromley Rock Provincial Park
- 24191 Yellow Lake: Hwy 3A, between Kaleden and Keremeos
- 28071 Big Bar: Hwy 97 at the Big Bar Rest Area
- 29093 Pothole Lake: Hwy 97C, 7 km east of Aspen Grove
- 29094 Brenda Mine: Hwy 97C at the Brenda Mine interchange
- 35093 Kimberley: Hwy 95A, 3 km south of Kimberley city centre
- 35094 Irishman: Hwy 3, 21 km south of Moyie
- 36191 Line Creek: Hwy 43 at Line Creek
- 37191 Blaeberry: Hwy 1, 15 km north of Golden
- 37192 Quinn Creek: Hwy 95, 8.6 km south of Parson
- 37291 Panorama: Toby Creek Road at the Panorama Fire Hall
- 38491 Blanket: Hwy 23S, 3.2 km south of Blanket Creek
- 39291 Goatfell: Hwy 3, 4.9 km west of Curzon Junction
- 41091 West Twin Creek: Hwy 16, near east end of West Twin Creek bridge
- 41095 Slim Creek: Hwy 16, 400 m east of Slim Creek Rest Area
- 43092 Tupper: Hwy 2, just east of the Hwy 52 Junction
- 44092 South Taylor Hill: Hwy 97 at the South Taylor Hill Chainoff Area
- 44093 Powell Road: Hwy 29 at Powell Road, east of Hudsons Hope
- 45091 Fort Fraser Hills: Hwy 16, 5 km east of Fort Fraser
- 45092 Spencer Pit: Hwy 27 at Spencer Pit, south of Fort St. James
- 46191 Yellowhead: Hwy 16, 1 km west of the Alberta border
- 54092 Trout Creek: Hwy 16, 22 km northwest of Smithers
- 55092 6 Mile Hill: Hwy 16, 39 km west of Burns Lake
- 64092 Menzies Hill: Hwy 19, 7 km southeast of Roberts Lake
