Farm buildings and access - 2.4 Farm building pest management
Pests that inhabit farm buildings can cause contamination.
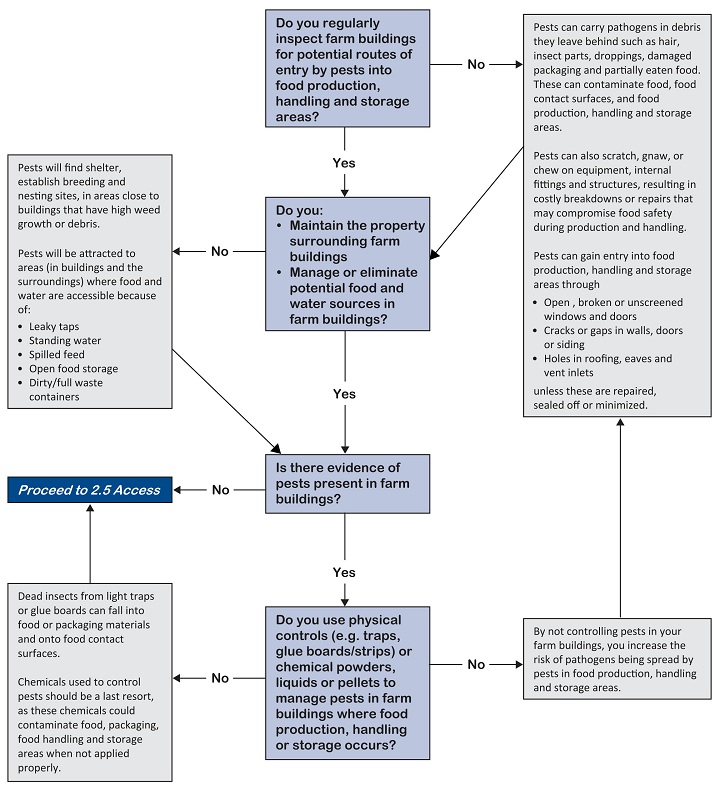
This good agricultural practice applies to farm buildings. Examples of pests include rodents, insects, flies, wildlife.
What needs to be done
Control pests within farm buildings.
How to do it
Pest management practices can be established for your operation or services can be contracted out to a qualified pest control officer.
Pest assessment
Check for signs of pests, including droppings, nesting and feeding opportunities, burrows, gnaw marks, sounds and odours.
Assess buildings for potential routes of entry by pests.
Prevention and habitat management controls
Minimize or prevent entry:
- Seal cracks or openings around foundations, walls, door frames and under doors
- Install screens for vents, eaves and windows
- Repair broken windows, roofs, walls and sidings
Manage potential breeding and nesting sites:
- Discourage roosting of birds with the use of porcupine spikes, fine netting or similar material
- Remove debris and control weeds and other vegetation in a 30?45 cm (12-18 in.) border surrounding the facility to eliminate sources of shelter that could be used for hiding, resting or nesting
Reduce sources of food and water:
- Repair leaky taps and pipes and ensure a good drainage system is in place to avoid standing water in and around buildings
- Store potential food sources, such as grain, feed, fruit or vegetables, securely to prevent pest access
- Remove or clean any spilled material, such as human food or livestock feed, that can be used as a food source by pests
- Keep garbage containers covered, closed or away from the facility to help limit pest access
- Remove garbage, organic waste and/or deadstock in a timely fashion to minimize potential food sources for pests
Physical controls
- Choose the appropriate physical control (for example, traps, glue boards/strips or other devices) for the pest, and use according to label instructions
- Avoid hanging sticky/glue traps directly above exposed food or packaging materials
- Locate light traps away from exposed food or packaging materials
- Use covered bait stations to ensure other animals cannot access the bait
Chemical controls
- To minimize potential cross-contamination, use chemical control only when necessary
- Use only products registered in Canada
- Choose the appropriate chemical control (for example, powder, liquid or pellet) for the pest
- Mix and use the product according to label instructions for the pest specified on the label
- Locate pest control products away from areas where they may cross-contaminate food or packaging materials
- Label all chemical containers and stations clearly with appropriate warnings
- Consider drawing a map to help identify and track locations where chemicals were applied
Pest disposal
Wear gloves to avoid direct contact when handling live or dead pests as well as used pest control products. Dispose of dead pests in a manner that will prevent further contamination.
Monitor pest management practices
Evaluate pest management practices at regular intervals by observing if there is a pest population reduction/elimination. Adjust practices if necessary.
Monitor pest control devices to ensure that they are in good repair and working order. If using bait, ensure that fresh or sufficient amounts are applied.
Records to keep
Keep a farm building pest management record or your own record that includes:
- Date
- Name of chemicals or type of devices used
- Observations (e.g. station, status) and action taken
- Initials of worker and/or company
If you need an audit
Be prepared for the auditor to:
- Review farm building pest management records
- Review records of training and certification of workers
- Observe location of pest control products and devices
Laws and regulations
There are few laws that impact on food safety requiring a pest control program for agricultural production. For example, laws about noxious weeds do not have a food safety implication. Generally, pest control requirements are laid out in laws regarding the processing of meat, fish and other food products, which have many provisions to prevent rodent and pest habitat and other measures to ensure pest control methods do not contaminate food:
- The Milk Industry Standards Regulation, Reg. 464/81 under the Milk Industry Act requires flies be kept under control at all times in dairy farms, and all rodents, birds, animals and insects be prevented from entering milking parlours and milking rooms, and that screens be used in the milk houses, no animals other than cows or goat be permitted in any building used for stabling or milking, and no animals or fowl be permitted in the milk houses, (s. 10 (8), s. 14 (2), s. 22 (12), s. 25 (8) (b), s. 30). Learn more about cleaning and sanitizing
- All pest control products used on-farm should be authorized for agricultural production, approved under various federal and provincial laws and not prohibited under these laws or regulation, and sold in accordance with these laws, for example the requirements of the Integrated Pest Management Act, S.B.C. 2003, c. 58, P2, Integrated Pest Management Regulation, Reg. 604/2004, and Hazardous Products Act (Canada), R.S. 1985, c. H-3
- Pest control products must not cause contamination of foods that are listed in the Food and Drugs Act (Canada), R.S. 1985, c. F-27, Food and Drug Regulations, Division 15. Under the Food Safety Act, S.B.C. 2002, c. 28, Meat Inspection Regulation, Reg. 349/04, food animals are inspected against the standards related to food safety and animal health established under the Food and Drugs Act (Canada) and the Meat Inspection Act (Canada)
- The Integrated Pest Management Act, S.B.C. 2003, c. 58, s. 3 (1) (c) specifies that no person shall use a pest control product except in accordance with the label for that product
- The Pest Control Products Act, 2002, c. 28, s. 6 prohibits the manufacture, storage, display, distribution or use of pest control products under unsafe conditions or contrary to the regulations. Certain pesticides may be prohibited under any circumstances
